Cartographer FAQ
Contents |
Cartographer Project FAQ
This FAQ for the Cartographer project is broken into several sections. If you do not find the answer to your question here, please let us know by emailing info1 -at- krupczak.org
Project
What is Cartographer?
Cartographer implements a novel approach to managing distributed systems by automatically discovering and tracking the relationships between its component systems and applications. Cartographer does so via specially designed agents -- residing on clients, servers and (potentially) network devices -- that detect, identify, and track the inter and intra-system dependencies or relationships. Dependencies include network level services like DNS, DHCP, and SMTP as well as higher-level application abstractions like filesystems, databases, directory services, telephony, and middleware.
Relationships are modeled using a dependency graph borrowed from the Graph Theory branch of mathematics. In our model, systems and applications are represented as vertices and dependencies are represented as edges. More specifically, we use directed graphs to indicate dependencies between clients and servers or between peers. Once dependencies are discovered, Cartographer agents automatically organize systems and applications into peer-to-peer overlays. Then, peers exchange management information amongst themselves to detect and correct service problems with the goal of doing so without the active participation of management software.
What license agreement is Cartographer released under?
Two licenses cover different components of Cartographer. The first, the GNU GPLv2, covers pieces that have been open sourced. The second, this license agreement covers those portions not released under open source.
What are the pieces parts?
The figures below depict the software architectural relationship between the various components. Green denotes an open-source component, covered by the GPLv2, while blue denotes those that are traditional or closed-source covered by our own license agreement.
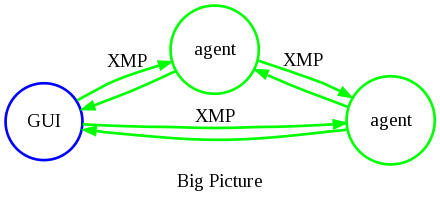
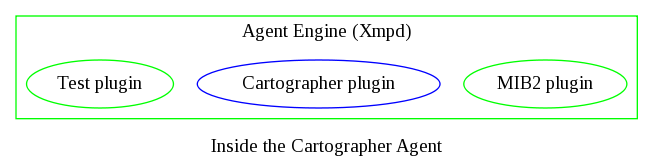
Where can I download the source?
See this web page to download source and binaries. http://www.krupczak.org/index.php/Distributions
What is the current version?
The current release is 1.1.
XMP
What is XMP?
XMP is an acronym for the not-very-creatively named XML Management Protocol. It is the management protocol used by the Cartographer project.
Where can I get it?
You can download XMP implementations here.
Do you have an implementation of XMP in my favorite programming language?
The answer depends on what your favorite programming language is. Implementations exist for C and Java with Python and Perl in the works.
Does XMP interoperate with SNMP?
Not directly. XMP borrows heavily from the Internet Management Framework SMI but the XMP protocol is TCP based and uses XML for data description and data transfer. SNMP uses UDP and ASN.1/BER for data description and transfer.
Is XMP secure?
We think so and hope so. XMP uses SSL for privacy and authentication.
Why didn't you just use SNMP?
Several reasons. First, SNMPv1 is not secure providing neither privacy nor authentication. Second, SNMPv3, while secure, is not so simple anymore. Third, since XMP was designed for a different purpose (e.g. distributed system dependency propagation and exchange of larger amounts of management information), the engineering and design choices driving the SNMP use of UDP were no longer relevant.
Installation
How do I install Cartographer?
Cartographer consists of two major components -- intelligent agents, and a graphical user interface. Instructions for installing the agent can be found here. Instructions for installing the graphical user interface can be found here.
Do you have a windows installer for Cartographer agents?
Yes! Have no fear. You too can mindless click Next Next Next. See this page for an overview.
Does the agent installer include binaries for all platforms?
Yes. Cartographer agents are self-upgrading and thus each installing contains binaries and libraries for all supported platforms. Self-installation functionality is under development.
How do I Uninstall Cartographer?
If you installed the Cartographer agent using the Windows installer, simply run the un-installer.
Do you have Solaris packages and Linux RPMs?
Solaris packages and Linux RPMs are under development.
Configuring Cartographer
What port do Cartographer agents listen on?
Cartographer agents listen on TCP/5270. This port is registered with [[1]].
How do I open a hole in my firewall for Cartographer?
For Linux iptables, the following rule allows XMP into and out of a system.
# allow TCP connections into port 5270 $IPTABLES -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 5270 --syn -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT # allow TCP connections out to port 5270 $IPTABLES -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 5270 --syn -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT
For Windows, you can add a rule for TCP port 5270 or create a firewall rule for the application xmpd-win32.exe.
How do I start and stop the Cartographer agent?
On UNIX, run the /etc/init.d script to start and stop the Cartographer agent.
/etc/init.d/cartographer
Usage: cartographer {start|stop|restart}
On Windows, simply use the Services control panel applet to start and stop the Cartographer agent.